This will help the juices redistribute and the roast to retain its tenderness. Usually, accountants are employed to manage and conduct the accounting tasks required by the accounting cycle. If a small business or one-person shop is involved, the owner may handle the tasks, or outsource the work to an accounting firm. Sole proprietorships, other small businesses, and entrepreneurs may not follow it. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.
The Adjustment Process
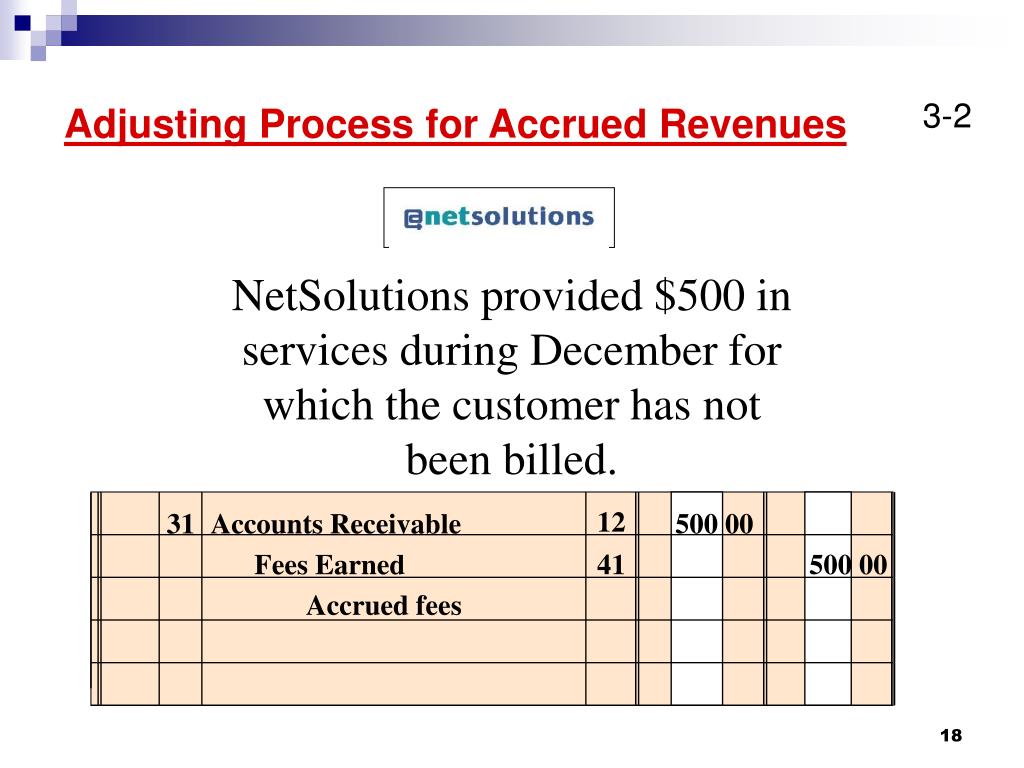
Previously unrecorded service revenue can arise when a companyprovides a service but did not yet bill the client for the work.This means the customer has also not yet paid for services. Sincethere was no bill to trigger a transaction, an adjustment isrequired to recognize revenue earned at the end of the period. For example, a company pays $4,500 for an insurance policycovering six months.
Adjusting Entries
Salaries Expense increases (debit) and Salaries Payableincreases (credit) for $12,500 ($2,500 per employee × fiveemployees). The following are the updated ledger balances afterposting the adjusting guide to using xero accounting entry. The salary theemployee earned during the month might not be paid until thefollowing month. For example, the employee is paid for the priormonth’s work on the first of the next month.
Accrual Accounting
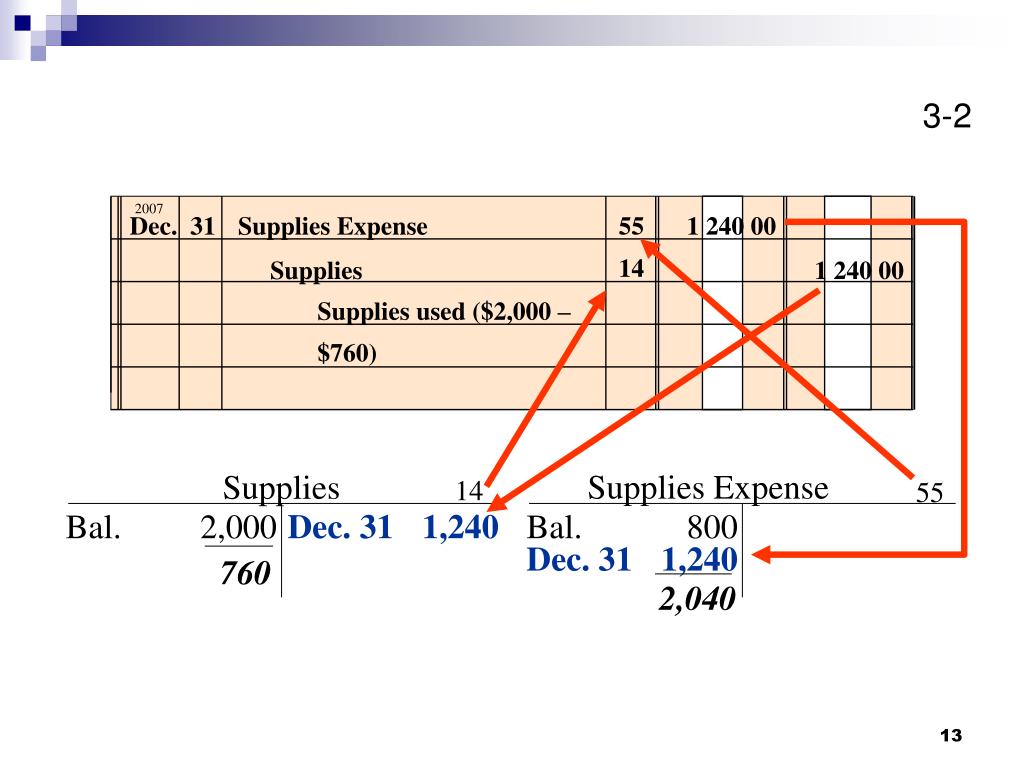
Not all accounts require updates, only thosenot naturally triggered by an original source document. There aretwo main types of adjusting entries that we explore further,deferrals and accruals. Let’s say a company has five salaried employees, each earning $2,500 per month. In our example, assume that they do not get paid for this work until the first of the next month. Accrued expenses are expenses incurred in a period but have yet to be recorded, and no money has been paid. Accrued revenues are revenues earned in a period but have yet to be recorded, and no money has been collected.
- During the accounting cycle, many transactions occur and are recorded.
- We also discuss the purpose of adjusting entries and the accounting concepts supporting their need.
- Make sure to check the roast periodically to ensure it’s cooking evenly and not drying out.
- The expenditure was initially recorded into a prepaid account on the balance sheet.
There are two main types of adjusting entries that we explore further, deferrals and accruals. As one can see on each year’s balance sheet, the asset continues to be reported at its $150,000 cost. However, it is also reduced each year by the ever-growing accumulated depreciation. The asset cost minus accumulated depreciation is known as the book value (or “net book value”) of the asset. For example, at December 31, 20X2, the net book value of the truck is $50,000, consisting of $150,000 cost less $100,000 of accumulated depreciation.
For example, let’s say a company pays $2,000 for equipment that is supposed to last four years. The company wants to depreciate the asset over those four years equally. This means the asset will lose $500 in value each year ($2,000/four years). In the first year, the company would record the following adjusting entry to show depreciation of the equipment. Depreciation may also require an adjustment at the end of the period.
You will learn more about depreciation and its computation in Long-Term Assets. However, one important fact that we need to address now is that the book value of an asset is not necessarily the price at which the asset would sell. For example, you might have a building for which you paid $1,000,000 that currently has been depreciated to a book value of $800,000. However, today it could sell for more than, less than, or the same as its book value. The same is true about just about any asset you can name, except, perhaps, cash itself.
The company may also enter into a lease agreement that requires several months, or years, of rent in advance. Each month that passes, the company needs to record rent used for the month. Taxes are only paid at certain times during the year, not necessarily every month. Taxes the company owes during a period that are unpaid require adjustment at the end of a period. Accounts Receivable increases (debit) for $1,500 because the customer has not yet paid for services completed.
